Point Process Modeling as a Framework to Dissociate Intrinsic and Extrinsic Components in Neural Systems
Grant Fiddyment
Graduate Program for Neuroscience
Boston University

Chapter 1.
Chapter 2.
Chapter 3.
Chapter 4.
Chapter 5.
Point Process Generalized Linear Model (GLM)
Analyze spatiotemporal patterns during seizure
Define "enhancement" & analyze in 3 data sets
Cluster neurons by functional profile in 2 data sets
Conclusion
Chapter 1.
Introduction
Modeling in Neuroscience


Okatan et al., 2005
Traub et al., 2005

"Bottom-Up"
"Top-Down"
Phenomonological
Point neuron
Biophysical
Compartmental neuron
Modeling in Neuroscience




Okatan et al., 2005

Traub et al., 2005


"Bottom-Up"
"Top-Down"
Phenomonological
Point neuron
Biophysical
Compartmental neuron

Point Process GLM
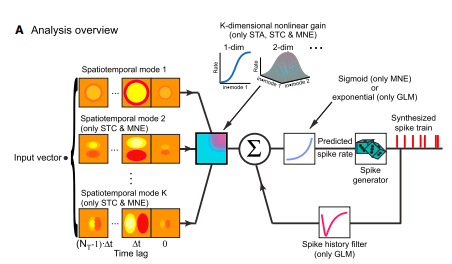
modified from Aljadeff et al., 2016
Input: Factors related to spiking
Output: Spike train
0 or 1

Stimulus*
* not used in Ch. 2-4
Network
Oscillations*
Self-history
Chapter 2.
Two categories of ictal discharges propagate with different spatiotemporal dynamics during human seizure
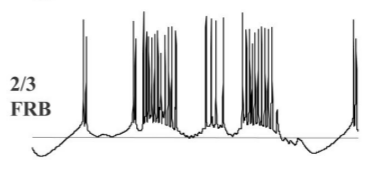
Spike-wave seizure
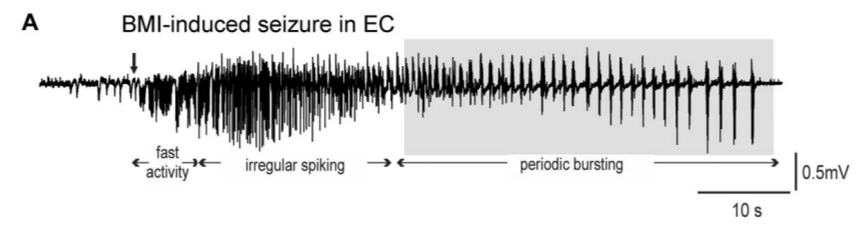
Huberfeld et al., 2011
Boido et al,. 2014
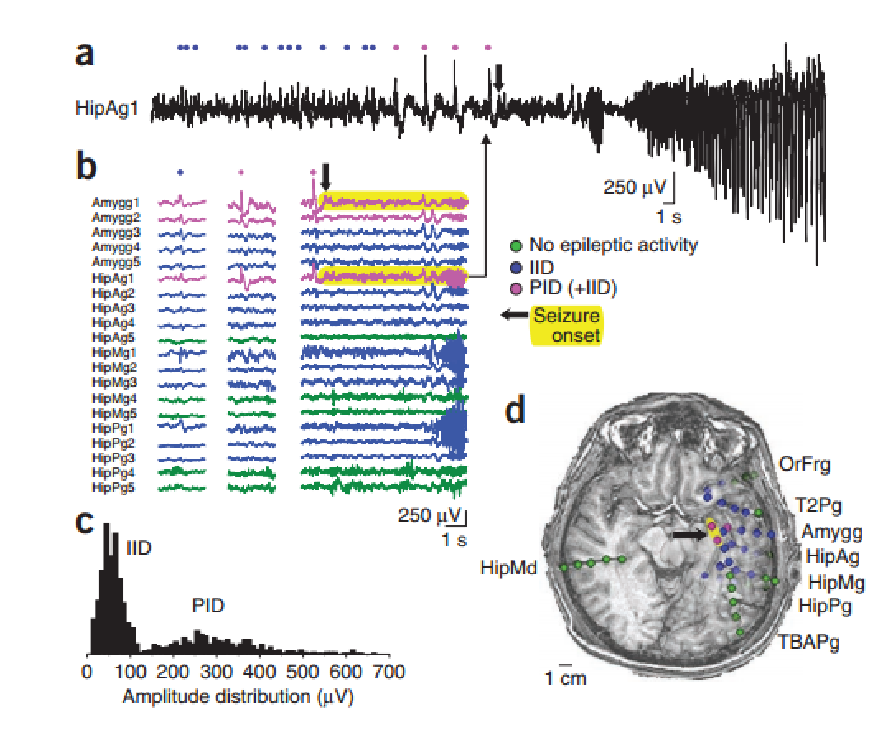
*
*
* Discharges are on the scale of ECoG, not LFP
Kramer & Cash, 2012
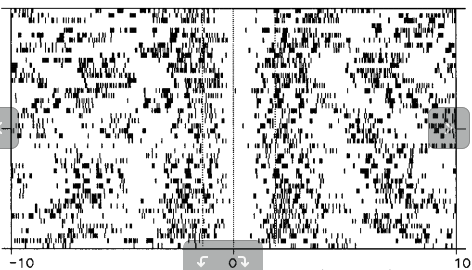
Spike-wave seizures
Microelectrode array: 4mm x 4mm, 96 electrodes
4 patients, 11 seizures
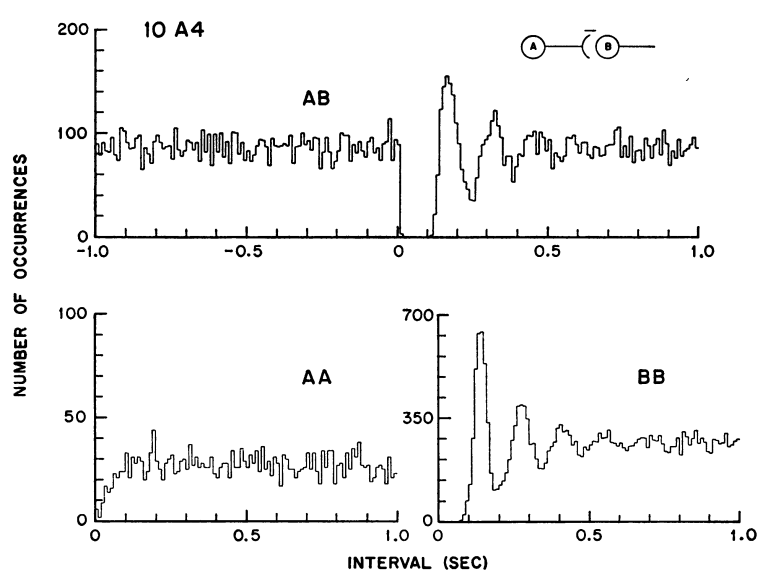
Two classes of discharge?
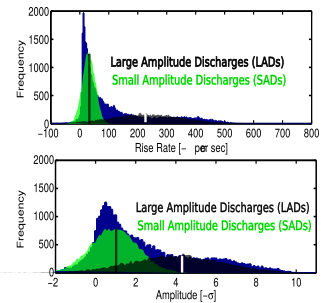


Ictal Discharge Statistics
| Totals (N=11 seizures) | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|
| Seizure duration (sec) | 73.73 | 18.76 |
| IDs per electrode | 679.53 | 230.88 |
| IDs per electrode per sec | 8.92 | 2.3 |
| LADs per electrode per sec | 3.88 | 0.98 |
| SADs per electrode per sec | 5.04 | 1.59 |
Methods
-
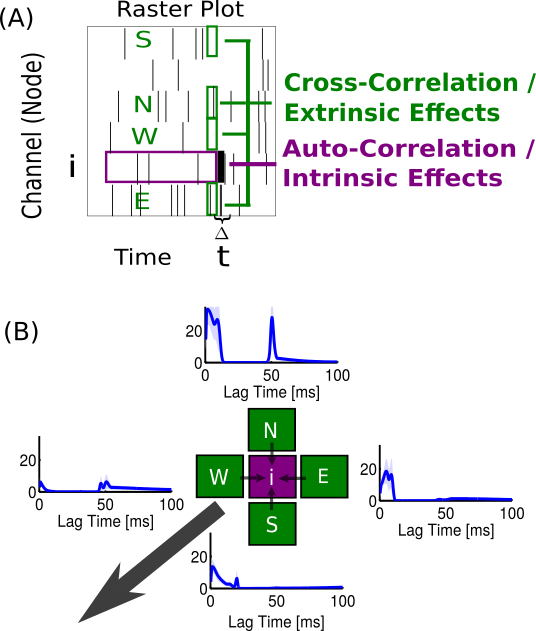
Analyzed over moving windows
(30 sec long, 1 sec step)- Auto/cross-correlation
- Point process model of LADs
-
Point process model of SADs
-
Considered spatial coupling (cross-corr. & extrinsic effects) from 4 nearest neighbors. (Modeled only 64 interior electrodes)
-
Directional analysis:
- Avg coupling in each direction (1-10ms)
- Compute composite direction
- Estimate distribution, Rayleigh z-test
Correlations
Correlations

Confounding: The Problem with Correlation
Moore 1970
GLM addresses this: see Chornoboy et al., 1988; Okatan et al., 2005; Kim et al., 2011
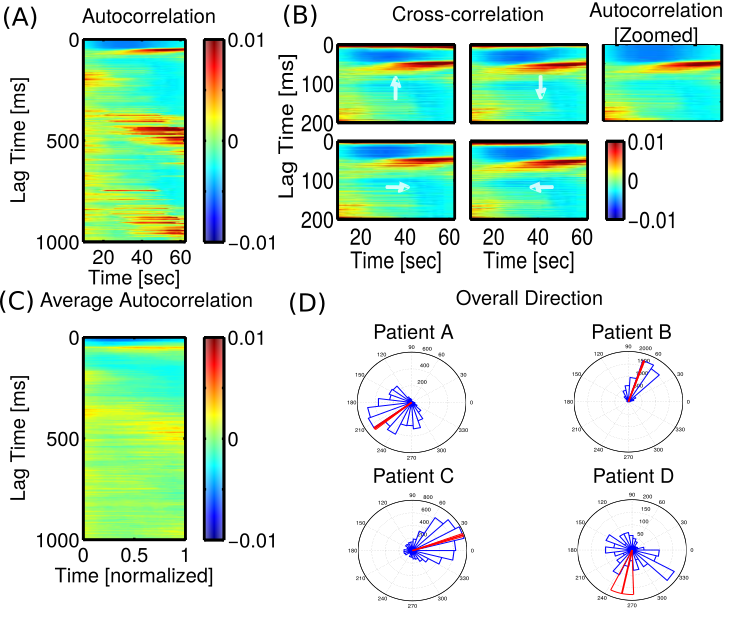
GLM Estimates (LADs)
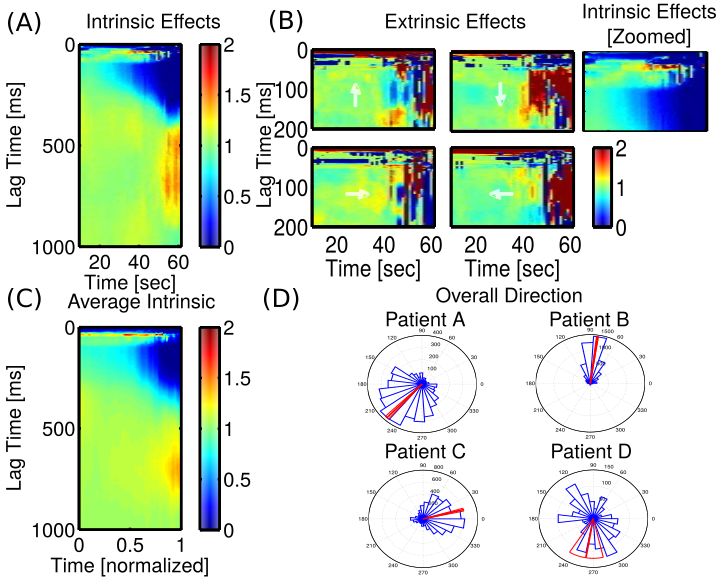
GLM directions match cross-correlation, for short lags
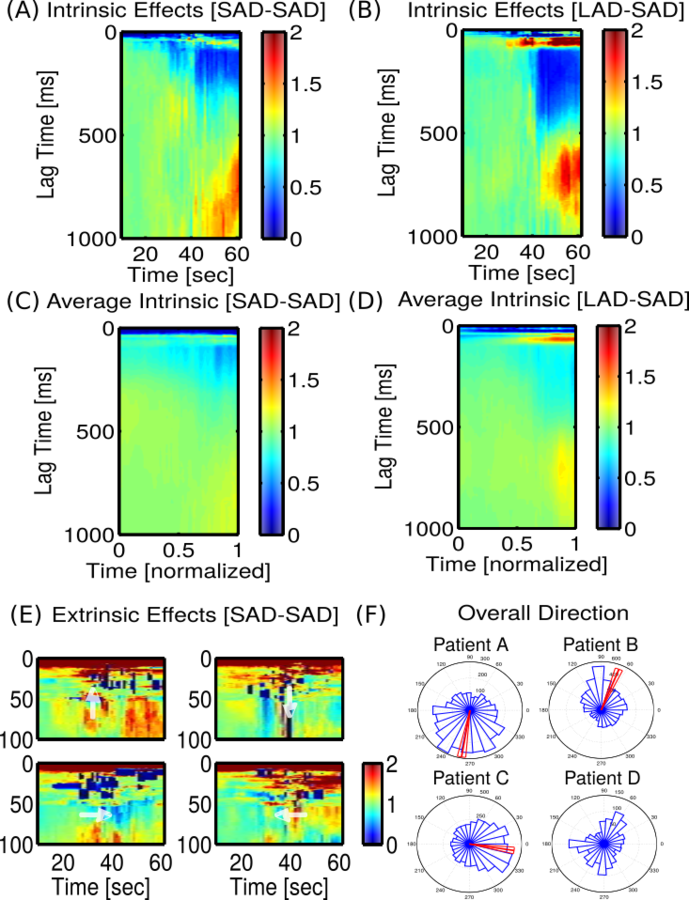
GLM Estimates (SADs)
SAD direction matches LAD, less concentrated
SAD-SAD
LAD-SAD

Conclusions
- Auto-correlation & GLM reveal signatures of rhythmic bursting.
50 ms time scale: K+ currents? (Bazhenov et al., 2004; Somjen et al., 2009)
500 ms time scale: GABA synapses? (Boido et al., 2014)
- GLM reveals SADs consistently follow LADs by 50 ms. Bursts with multiple SADs occur for some patients, not all.
- Cross-correlation & GLM reveal consistently directional propagation for LADs, weaker directional propagation for SADs but same angle. Unclear whether spatial effects are similar at longer lags (>10 ms)
- Unlike auto/cross-correlation, GLM intrinsic/extrinsic effects are not confounded. Extrinsic effects differ by direction
Chapter 3.
Point process modeling reveals a unique type of enhancement during human seizures
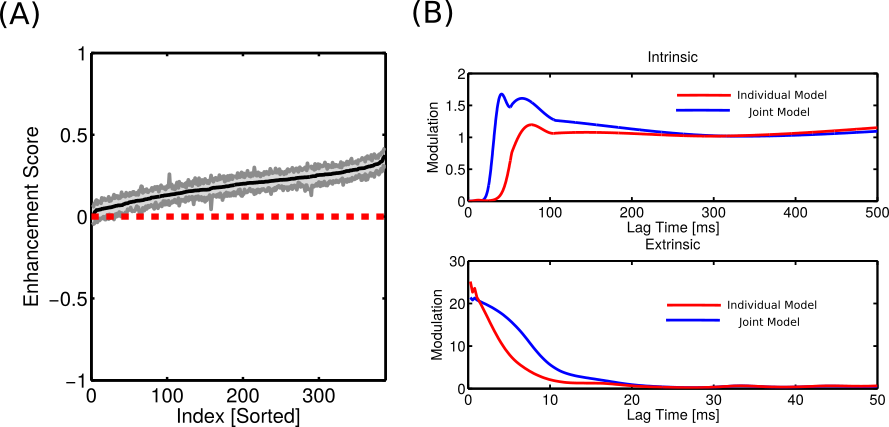
How much info does each neuron provide?
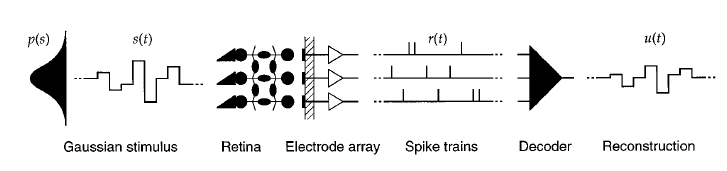
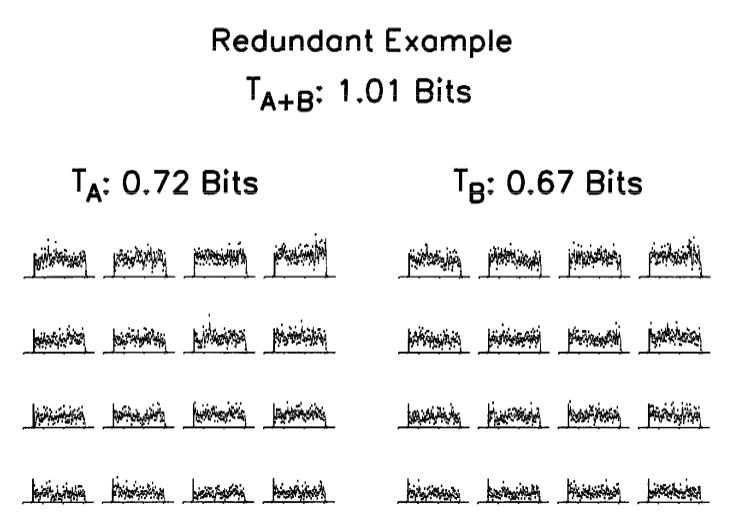
Warland et al., 1997
"Mutual information"
Joint model
Individual models
On/On Cells: Redundant
On/Off Cells: Independent
How much info does each factor provide?

modified from Aljadeff et al., 2016

Stimulus
Network
(Extrinsic)
Oscillations

Self-history
(Intrinsic)
Multivariate mutual information
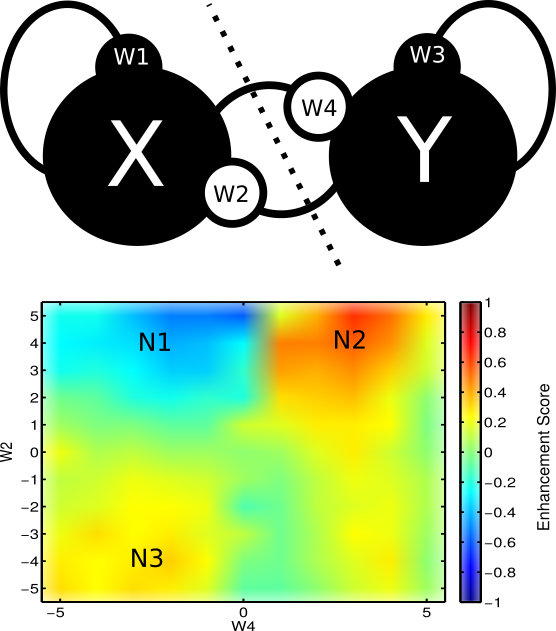
A curious phenomenon
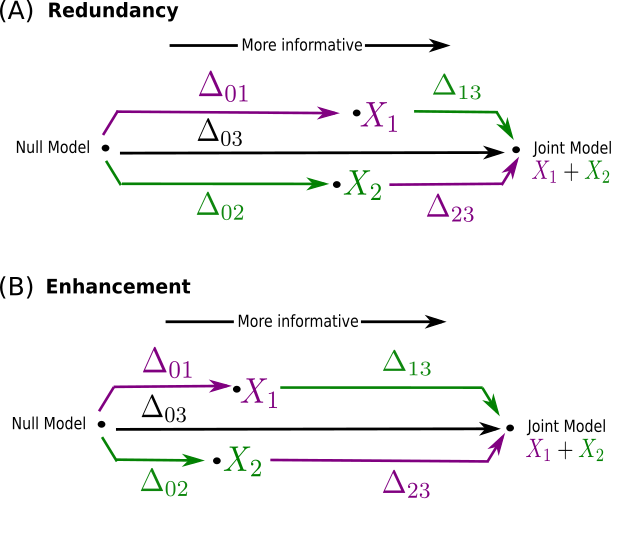
X1: Intrinsic Effects, X2: Extrinsic Effects
Enhancement score
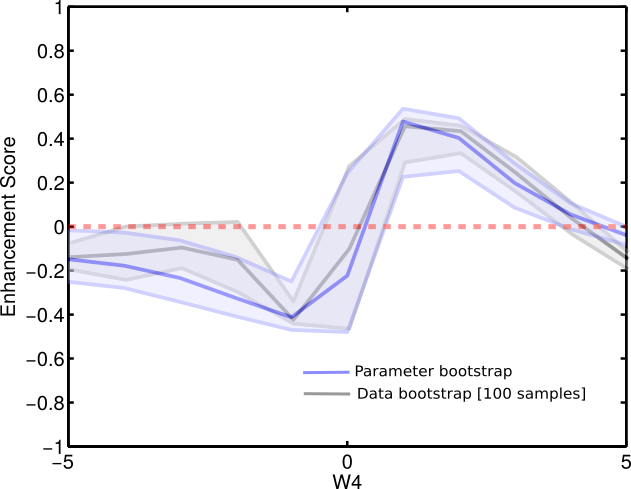
Assess confidence by data bootstrapping
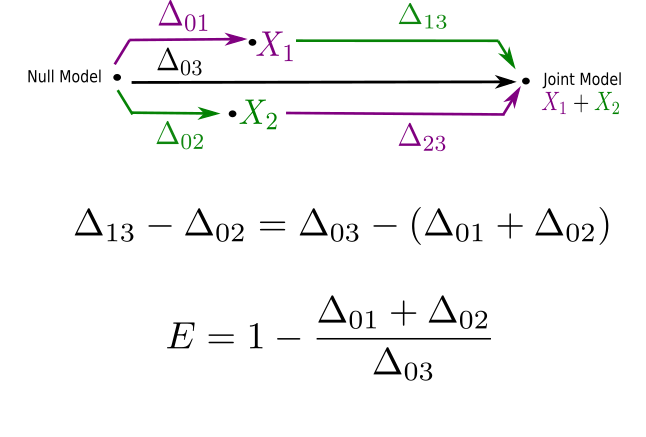
Negative: Redundancy
Positive: Enhancement
Simulated network
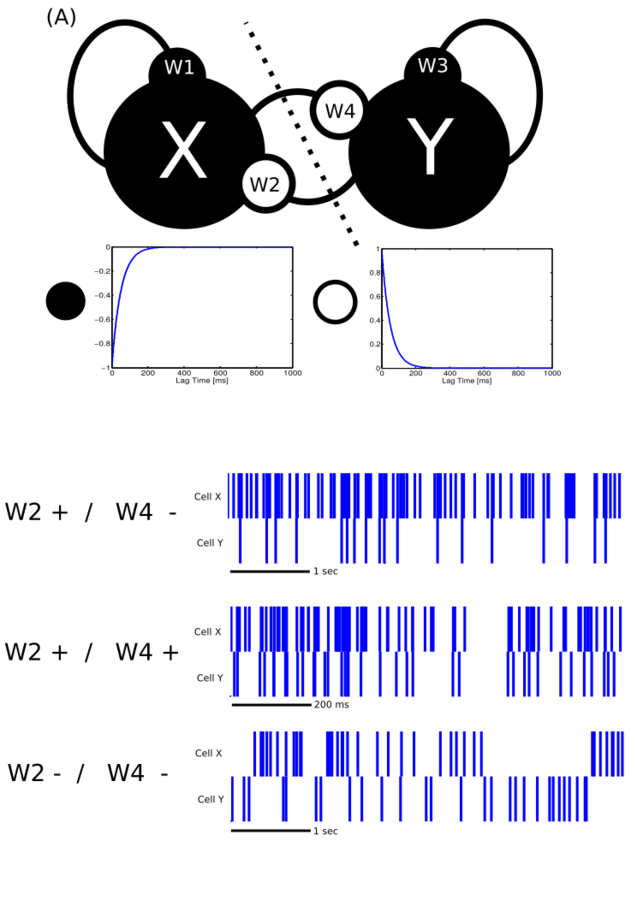
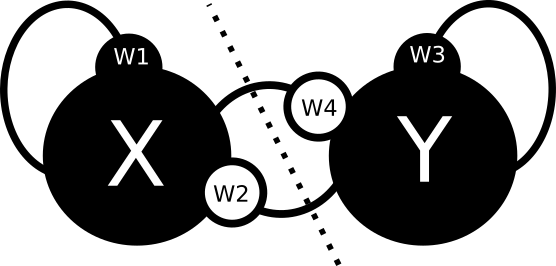
Enhancement/redundancy depend on system feedback

Enhancement/redundancy depend on system feedback
Seizure: Enhancement between intrinsic/extrinsic
Mouse auditory network data
Thanks to Nicholas James!
Auditory cortex
Prefrontal cortex
500 ms noise,
~1 sec trial
100 trials per block
Mouse auditory networks: Redundancy between I/E
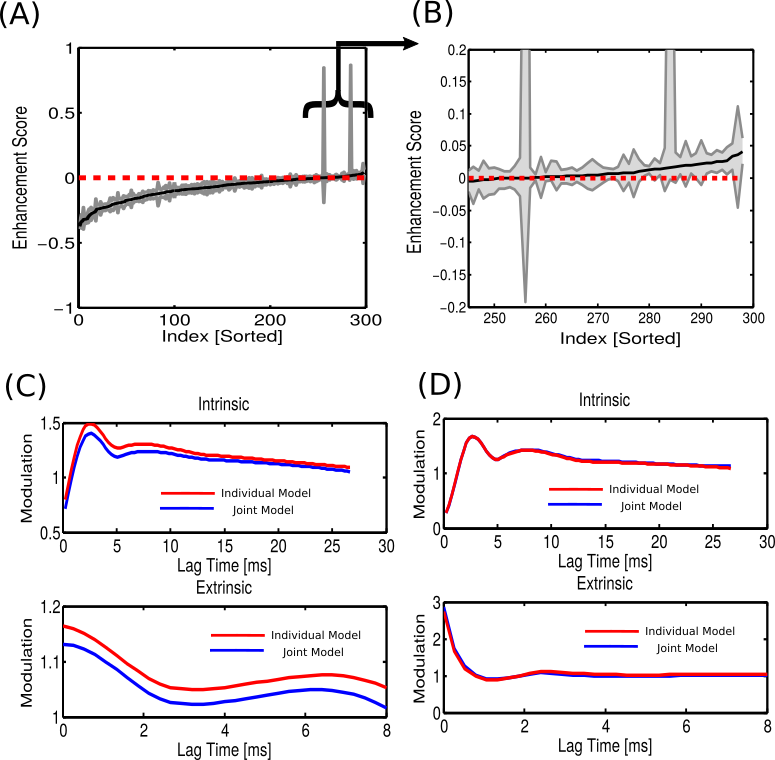
Why redundancy?
-
Perhaps intrinsic & extrinsic effects are just implicitly capturing stimulus effect.
- Extrinsic network too large? Larger networks have more info, more redundancy [Shadlen & Newsome, 1998; Schneidman et al., 2003; Quian Quiroga et al,. 2007]
Why enhancement?
- May reflect combined excitation & inhibition (Boido et al., 2014)
Conclusions
- Enhancement score, computed from GLM deviances, is a measure of mutual information.
- Confidence intervals for enhancement score can be estimated by bootstrapping.
- Enhancement b/w intrinsic/extrinsic effects is observed in MEA during seizure. This may reflect combined excitation + inhibition.
- Redundancy b/w intrinsic/extrinsic effects is observed in mouse auditory/prefrontal cortex during passive listening. This may reflect stimulus effects and/or a general lack of coupling.
Chapter 4.
Point process modeling reveals a heirarchy of functional cell types based on self-history dependence
GLM filters differ by cell type
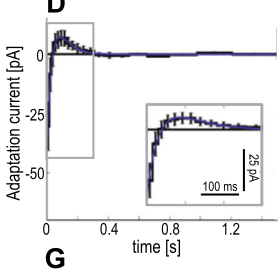
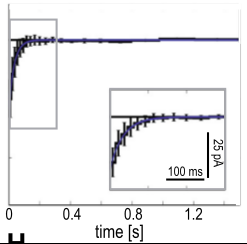
Fast-Spiking (FS) Cells
Non-FS Cells
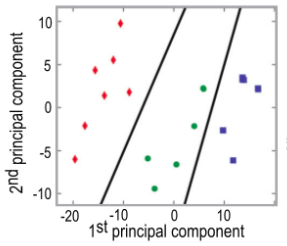
Regular Spiking (E)
FS (I)
Non-FS (I)
Mensi et al., 2012
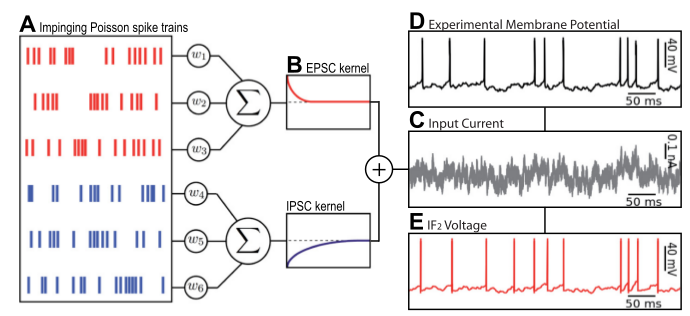
"The question arises whether a more principled characterization and classification of the cell types is possible based on the properties affecting the conversion of synaptic inputs into a spike."
Spike data
BU Data:
Allen Cell Types Database:
GAD2+ & PV+ interneurons, 90 cells

Thanks to Joan Martinez!
Thanks to Allen Institute & UW!
1 sec
3 sec
10 cell types, 171 cells
http://celltypes.brain-map.org
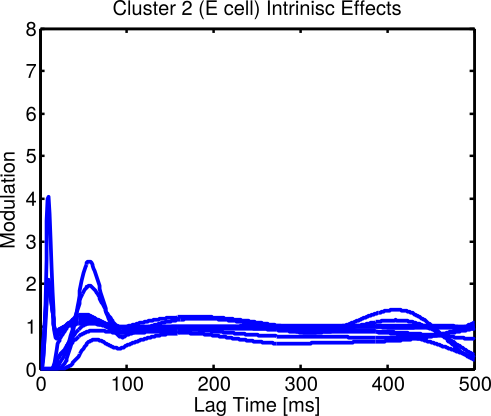
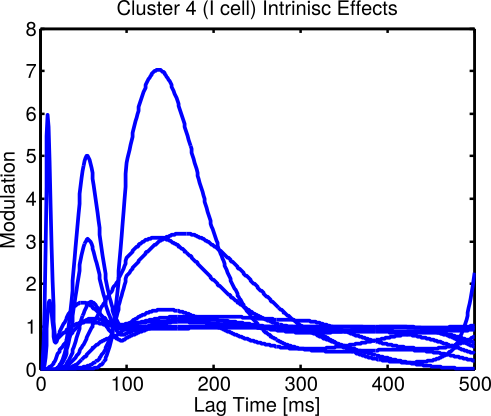
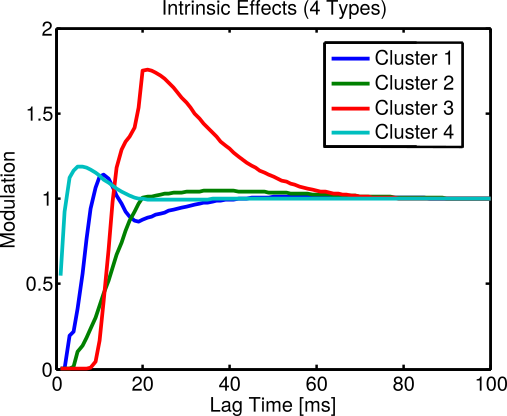
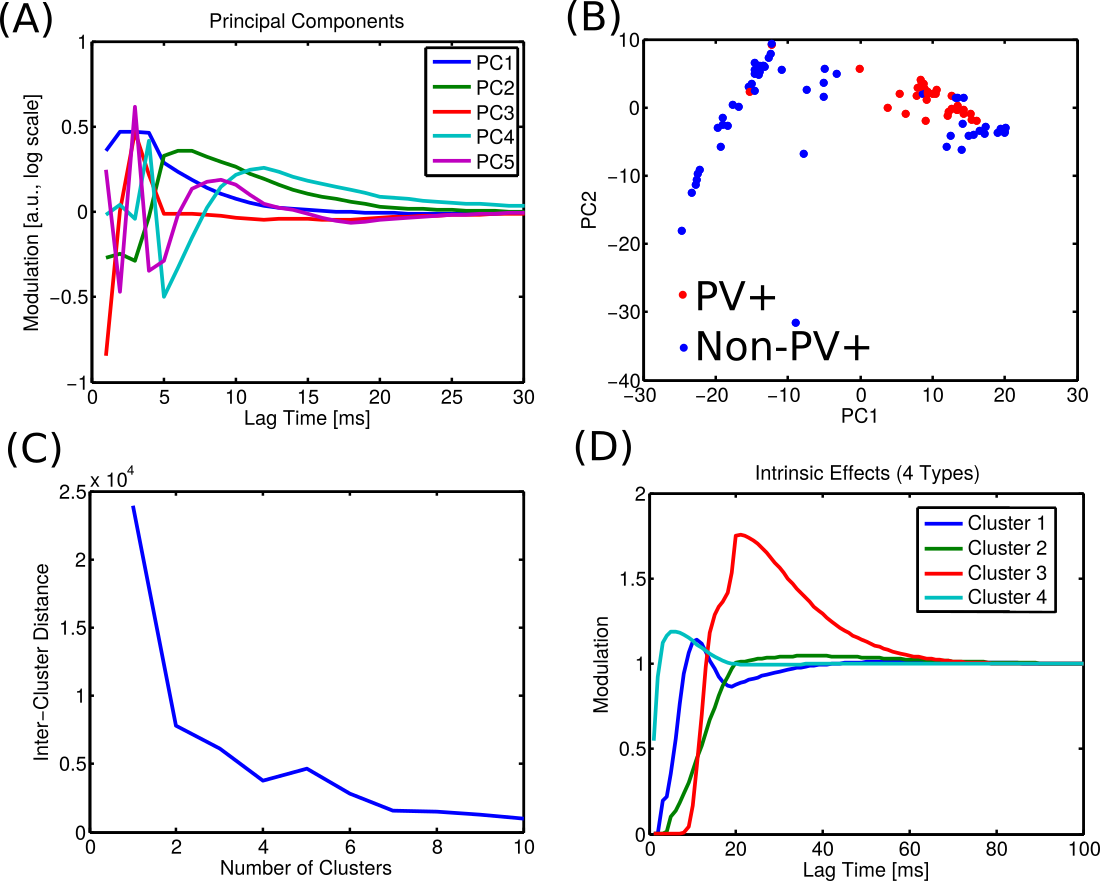
BU Data: Intrinsic effects successfully cluster
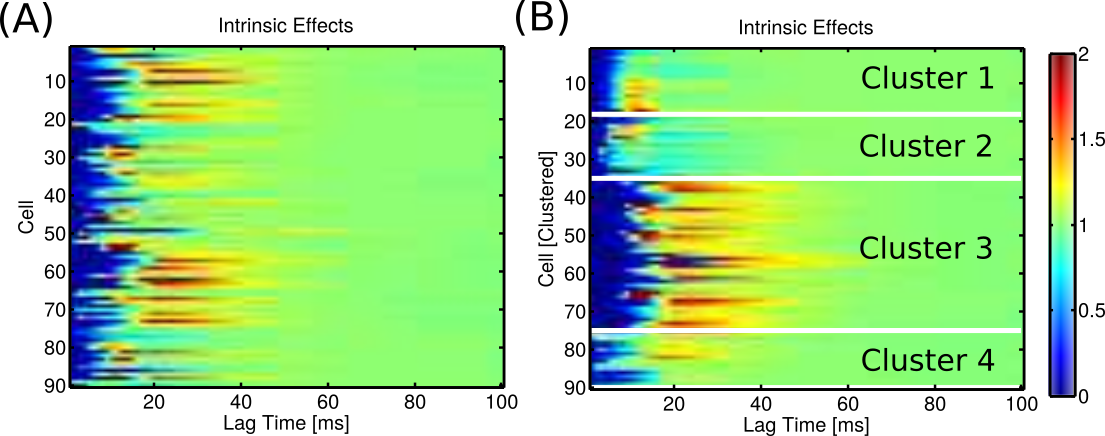
BU Data: Clusters align with cell type and hint at sub-types
| Cluster | # PV+ Cells (FS) | # Non-PV+ Cells |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | 3 |
| 2 | 14 | 3 |
| 3 | 2 | 38 |
| 4 | 2 | 13 |
| Total | 33 | 57 |
Electrophysiology & histology analysis also found four types (Martinez, 2015)
Allen Data: Intrinsic effects successfully cluster
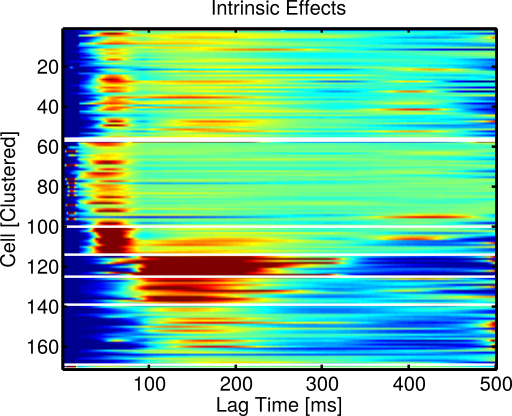
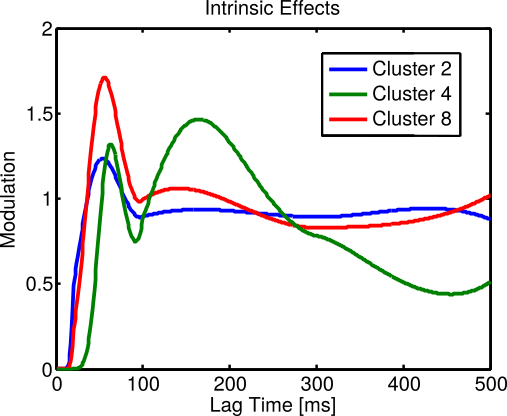
Cluster 4
Cluster 8
Cluster 2
Exc. cells
Inh. cells
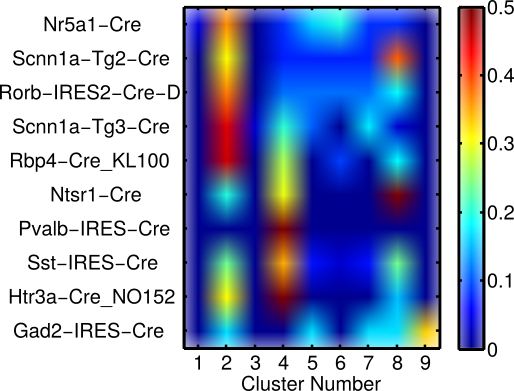
Total cells per cluster: 1, 55, 1, 43, 14, 11, 14, 30, 2
Allen Data: Clusters align with cell type and hint at sub-types
Conclusions
- Intrinsic effects are frequently predictive of genetic cell type.
- Futhermore, they may even reveal functional divisions within & among cell types!
e.g., Subset of SST (I) + NTSR (I) + SCNN1a-Tg2 (E) + Rorb-IRES2 (E) seem to comprise a distinct functional type with slow rhythmicity (100-200 ms, Cluster 8)
- Slower spiking (100-300 ms period) seems to characterize a number of cells. Careful stimulus design will be necessary to compare across more brain areas.
Chapter 5.
Conclusion
Innovation and Impact
-
Chapter 2: Extended point process GLM to a new kind of spike: Ictal Discharges. Estimated seizure- & patient-specific models of ID dynamics. Showed there are two types of ID by shape, but their dynamics (bursting, directionality) are similar.
-
Chapter 3: Defined intrinsic/extrinsic enhancement, a new kind of mutual information. Showed how to compute conf. intervals using GLM & a data bootstrapping procedure. Show I/E enhancement occurs during seizure.
- Chapter 4: Showed point process GLM can be used to classify neurons based on their functional spike output.
Future Directions
Chapter 2:
- Fit for more seizures and patients, analyze variability.
- Biophysical model, animal model >> Mechanisms!
Chapter 3:
- Relate enhancement to treatment strategies: Do high-enhancement nodes have greater network influence?
- Look for intrinsic/extrinsic enhancement during normal brain states, extrinsic/extrinsic enhancment between brain areas.
Chapter 4:
- Include more factors in clustering: network coupling, oscillatory dynamics, stim. response
- Which stim. protocol best elicits spike variability?
- Systematically deal with perfect predictors
Acknowledgements
Support:
- NIH / NINDS R01 NS073118
- NIH / NINDS R01 NS062092
- Epilepsy Foundation Grant 330118
- CompNet Travel Award
Boston University:
- Mark Kramer
- Uri Eden
- Nancy Kopell
- Jason Ritt
- Nick James [Ch. 3] (UCSF)
- Joan Martinez [Ch. 4] (Columbia)
- Manu Martinet (MGH)
- Kyle Lepage (Allen Inst.)
- Mikio Aoi (Princeton)
- Wei Tang
- Xinyi Deng (Columbia)
- Emily Stephen (MIT/MGH)
- Jason Sherfey
- Austin Soplata
- Stefania Sokolowski
MGH:
- Sydney Cash
- Omar Ahmed (UMich)
- Jason Naftulin
UC Davis / UGA:
- Andrew Sornborger
BU Data: Clusters align with cell type

Exc. cells
Inh. cells
Total cells per cluster: 1, 55, 1, 43, 14, 11, 14, 30, 2
Allen Data: Clusters align with cell type and hint at sub-types